Can Prostate Calcification Trigger Prostatitis?
In the realm of men's health, issues involving the prostate are especially common and often interrelated. Two conditions that frequently come up are prostate calcification and prostatitis. While prostate calcification is typically discovered incidentally during ultrasound exams and may not cause noticeable symptoms, prostatitis can result in considerable pain and discomfort. But is there a connection between the two? Can one lead to the other?
Let's take a closer look at what modern research and traditional medicine say about this relationship and how men can protect themselves.
What Is Prostate Calcification?
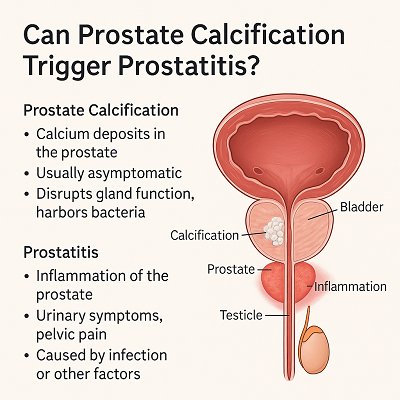
Prostate calcification refers to the buildup of calcium deposits in the prostate gland. These calcified lesions often form silently, without symptoms, and are usually discovered during routine ultrasound scans.
Causes of prostate calcification include:
Aging: Age-related changes in calcium metabolism can result in mineral deposits within the prostate.
Past inflammation: Previous episodes of prostatitis can leave behind sloughed-off epithelial cells and residual calcium and phosphate salts, which may later calcify.
While it may seem like a minor or incidental finding, prostate calcification isn't always harmless. In some cases, it can:
- Disrupt normal prostate fluid secretion
- Cause perineal discomfort due to pressure on surrounding tissues
- Act as a breeding ground for bacteria, increasing the risk of recurrent prostatitis
What Is Prostatitis?
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland, caused by infection (bacterial prostatitis) or other non-infectious factors (chronic pelvic pain syndrome). Unlike the silent nature of prostate calcification, prostatitis tends to be symptomatic and disruptive.
Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Painful urination or burning sensation
- Pelvic or perineal pain
- Painful ejaculation or erectile dysfunction
- Reduced libido and overall fatigue
Causes of prostatitis include:
- Bacterial infection, especially from organisms like E. coli or Staphylococcus aureus
- Poor lifestyle habits, such as prolonged sitting, excessive alcohol use, or frequent masturbation
The Connection Between Prostate Calcification and Prostatitis
Yes, prostate calcification can contribute to the development or recurrence of prostatitis—and vice versa.
- Calcified areas may harbor bacteria, serving as a nidus for infection. Once pathogens colonize these calcified zones, they can easily migrate into the prostate and trigger inflammation.
- Chronic prostatitis itself can lead to calcification, as persistent inflammation encourages the deposition of minerals within the gland.
This vicious cycle complicates treatment and increases the chances of chronic symptoms, making early intervention crucial.
The Dangers of Untreated Conditions
Impact on Sexual Health
Both prostate calcification and prostatitis can impair sexual function. Calcified tissue may interfere with nerve function and blood flow, leading to erectile dysfunction and painful intercourse. Chronic inflammation can reduce testosterone levels, causing decreased libido and performance anxiety.
Effect on Partners
If prostatitis is caused by sexually transmitted pathogens (e.g., chlamydia, mycoplasma, or trichomonas), it can pose risks to sexual partners, potentially causing gynecological infections.
Damage to the Urinary System
These conditions can also lead to:
- Prostate enlargement (BPH)
- Incomplete bladder emptying and residual urine
- Increased risk of urinary tract infections, cystitis, or even kidney infections
- Severe complications like hydronephrosis or uremia if left untreated
Mental and Emotional Burden
Symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, insomnia, and anxiety often accompany chronic prostatitis. These effects can interfere with work performance, social life, and overall mental health.
Treatment & Prevention Strategies
While antibiotics are commonly used for prostatitis, they're often ineffective against calcification and long-term inflammation. This is where herbal medicine offers a promising alternative.
Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill, a patented formula based on traditional Chinese medicine, is made from over 50 natural herbs. It has shown effectiveness in:
- Clearing heat and toxins
- Improving blood circulation
- Alleviating pain and inflammation
- Fighting fibrosis and calcification
- Enhancing urinary function
Because it can be tailored to each patient's condition and constitution, this formula supports a more personalized and comprehensive healing process. It also reduces the risk of recurrence and addresses both prostatitis and prostate calcification simultaneously.
Prevention Tips:
- Avoid prolonged sitting—stand up and stretch every hour
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Maintain good personal hygiene, especially around the genitals
- Stay sexually moderate and avoid risky behaviors
- Get regular prostate check-ups, especially after the age of 40
Final Thoughts
Prostate calcification and prostatitis are more than just isolated health concerns—they're deeply interconnected and can significantly impact a man's quality of life. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options empowers men to take control of their health.
With the right lifestyle adjustments and targeted therapies—such as the Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill—it's entirely possible to break the cycle of inflammation and restore long-term prostate health.



