If Epididymitis Develops into an Epididymal Cyst, Is Surgery Necessary?
When dealing with epididymitis, most men expect the discomfort to subside after a round of antibiotics or natural anti-inflammatory therapies. But for some, the situation evolves—what starts as inflammation becomes something more structural, like an epididymal cyst. This development often leads to one pressing question: Do I need surgery?
Let's break it down with a clear, practical view to help you understand your options and make informed decisions.
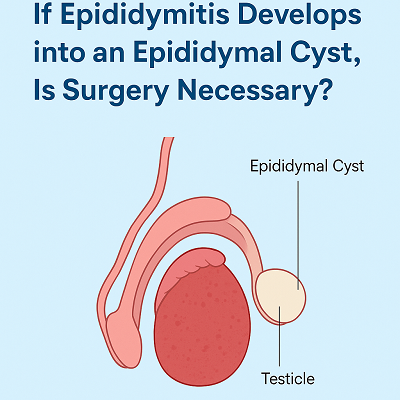
What Is an Epididymal Cyst?
An epididymal cyst, also known as a spermatocele, is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the epididymis—a tightly coiled tube at the back of the testicle where sperm matures. While it's often painless and benign, it can feel like a small lump or swelling in the scrotum, which understandably causes anxiety in many men.
These cysts are typically filled with a milky or clear fluid that may contain sperm. They can vary in size, and while many remain small and unproblematic, others may grow large enough to cause discomfort or a feeling of heaviness.
How Does Epididymitis Lead to a Cyst?
Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, often triggered by bacterial infection or even by non-infectious causes such as trauma or autoimmune responses. When the inflammation persists or recurs, it may damage the delicate ducts and tissues within the epididymis. As a result, fluid can accumulate, leading to cyst formation.
Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor. That’s why timely and effective treatment of epididymitis is essential—not only to relieve symptoms but also to prevent complications like cysts, infertility, or chronic pelvic pain.
Is Surgery Always Necessary?
Short answer: No, not always.
The decision to proceed with surgery depends on several factors:
When Surgery May NOT Be Needed
- The cyst is small and not growing.
- It causes no pain or only mild discomfort.
- It doesn't interfere with sexual or daily activities.
- There are no signs of infection or complications.
In such cases, conservative treatment and regular monitoring are sufficient. Many men live comfortably for years without needing surgery.
When Surgery May Be Considered
- The cyst is large and causes scrotal pain or pressure.
- It interferes with sexual function or urination.
- There's suspicion of malignancy (though rare).
- There are recurrent infections or inflammation that don't respond to medication.
The surgical procedure is typically called spermatocelectomy, which involves removing the cyst from the epididymis. It’s generally a low-risk outpatient surgery, but like all surgical interventions, it carries the possibility of complications such as infection, recurrence, or damage to sperm ducts.
Are There Non-Surgical Alternatives?
Yes. Before opting for surgery, many patients seek conservative approaches, especially those who wish to preserve fertility and avoid potential surgical risks. One effective route is traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), which offers a holistic, organ-targeted solution.
Herbal Therapy: Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill
The Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill is a natural herbal remedy commonly used to treat chronic epididymitis and prevent complications such as cyst formation. It works by:
- Clearing heat and toxins from the urogenital system
- Reducing inflammation and relieving pain
- Promoting blood circulation and tissue repair
- Inhibiting bacterial growth
- Supporting natural drainage of fluid accumulation
Unlike antibiotics or surgery, this formula addresses the root cause rather than just symptoms. Many patients with recurrent or chronic epididymitis have found long-term relief and cyst size stabilization with consistent use of this herbal approach—without disrupting fertility.
Learn more about how this herbal treatment works on our product page.
Watchful Waiting vs. Action
If you're diagnosed with an epididymal cyst, don't rush into surgery. First, get a clear understanding of your situation. If the cyst is painless and symptoms are mild, try herbal remedies or adjust your lifestyle, for example:
- Avoid prolonged sitting; remember to get up and move around.
- Wear loose-fitting underwear; avoid anything too tight.
- Be moderate with cycling; don't overexert yourself.
However, if the cyst is significantly impacting your quality of life or your symptoms are worsening, you should promptly consult a urologist. Get an ultrasound examination for a comprehensive evaluation. While surgery is a safe and effective option, it is definitely not the only one.
A Final Thought: Your Body, Your Choice, but Be Informed
Epididymal cysts can be alarming, but they don’t always require drastic intervention. With the right treatment path—whether surgical or natural—you can regain control over your reproductive health. If you're exploring herbal options, the Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill offers a time-tested, non-invasive alternative worth considering.
Have any questions? Feel free to chat with our TCM experts; they can provide personalized advice. Don't be afraid, take it one step at a time, and your body will surely get better!



