Can Physical Red Light Treat Prostatitis?
Many therapeutic devices are on the market to treat the prostate, but their effectiveness is controversial. As a relatively hot treatment device, is the efficacy of physical red light good? Can it treat prostatitis?
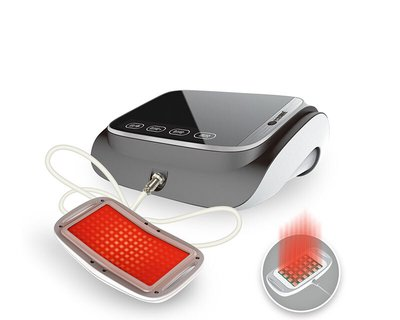
Red light therapy devices generally work through the lower abdomen and utilize heat production to relax the perineal muscles. The red light therapy device may be useful in restoring the relaxed pelvic floor muscles and, therefore, may be useful for some of the symptoms of prostatitis, such as pain and lower abdominal sagging and bloating.
Most prostatitis cases refer to chronic non-bacterial prostatitis, which is characterized by some painful symptoms and urinary abnormalities caused by excessive tension in the pelvic and perineal muscles. These symptoms include lower abdominal discomfort, testicular pain, painful ejaculation, perineal swelling, urinary frequency, urgency, incomplete urination, and increased nighttime urination.
These symptoms do not have much to do with the prostate or prostate infections. However, they are clinically thought to be related to poor lifestyle habits, such as prolonged sedentary behavior, staying up late, exertion, excessive mental stress, alcohol consumption, and exposure to cold. These factors can cause the pelvic floor and perineal muscles to be too tense, thus producing these clinical symptoms. Hence, the main thing is alleviating this through medication or physical therapy, relaxing the pelvic floor and perineal muscles, or reducing bladder overactivity.
From this point of view, the red light therapy instrument, as a means of physical therapy, may have a certain role in prostatitis. However, you must pay attention to the temperature and time when using it so as not to cause damage to the body.
It is also worth noting that the red light therapy device is only an aid and does not entirely cure prostatitis. The treatment of prostatitis needs to be based on its causes, which are generally of two kinds:
Bacterial Prostatitis: This type of inflammatory disease can be found in large numbers of white blood cells in the prostate fluid and is treated with effective antibiotics rather than counting on physical therapy. Commonly used antibiotics are quinolone antibiotics, such as levofloxacin, cephalosporin, such as cefaclor, and more novel antibiotics, such as Fosfomycin.
Non-Bacterial Prostatitis: It is mainly aseptic inflammation and swelling in the prostate; treatment includes alpha-blockers, such as tamsulosin, to improve the symptoms of pelvic floor pain; on the other hand, it can also be combined with traditional Chinese medicine to relieve heat and induce diuresis. Patients can also take the patent medicine Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill.
The medicine is formulated with a variety of herbs, with the main effect of clearing away heat and detoxifying the body, invigorating blood circulation, promoting vitality, relieving pain, and inducing diuresis for treating stranguria; it can relieve pain, eliminating inflammation, and comprehensively regulate the patient's urinary system, eliminate the lesions from the root, and restore the normal function of the prostate.
The clinic believes prostatitis has much to do with the patient's bad habits. Therefore, the treatment of prostatitis is indispensable for general treatment, and patients should do the following:
1. Avoid Holding Urine: Holding urine can overfill the bladder and compress the prostate, leading to poor blood flow, congestion, and swelling, as well as causing harm to the kidneys and ureters.
2. Avoid Sitting For a Long Time: Sedentary behavior is the main cause of prostatitis. Extended periods of riding a bicycle or motorcycle, with the seat repeatedly stimulating the prostate, can also lead to prostate congestion and inflammation.
3. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Tobacco and alcohol have stimulating effects on the prostate and urethra. Heavy smoking and alcohol can cause discomfort in the perineum and congestion of the prostate, which reduces the prostate's ability to resist disease.
4. Avoid Cold: The prostate is afraid of cold, and sustained cold stimulation can lead to long-term sympathetic nerve excitation, so the smooth muscle contraction results in prostatic duct obstruction, causing prostatitis aggravation.
You may also be interested in:
Common Queries About Prostatitis Treatment: Frequently Asked Questions
Prostate Health Tips: Avoid These Post Sex Mistakes for a Healthy Prostate
Swimming: Benefits of an Active Lifestyle for Men with Prostatitis



