Blood in Your Urine? Seminal Vesiculitis Could Be the Underlying Cause
Tarkey, 32, experienced a mild burning sensation while urinating. Mistaking it for a minor issue or "internal heat," he ignored the symptoms. The next day, he noticed pink-colored urine without pain. On the third morning, bright red blood streaks appeared at the end of his urine stream, accompanied by dull lower abdominal pain. Alarmed, he sought immediate medical help and was diagnosed with seminal vesiculitis. Urethral burning and blood in urine should never be ignored; prompt medical attention is essential.
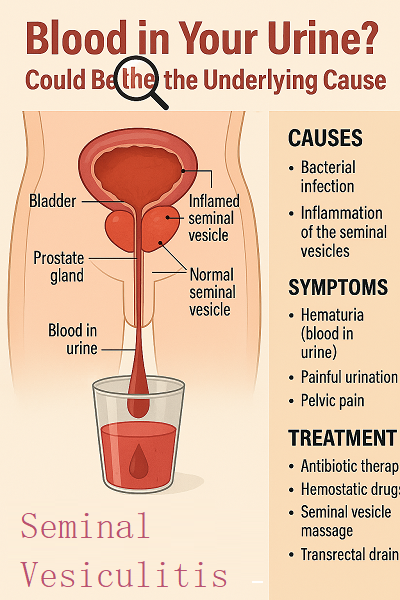
Why Seminal Vesiculitis Causes Blood in Urine
Seminal vesiculitis is a male reproductive system disorder primarily caused by bacterial invasion leading to purulent inflammation. This condition irritates the seminal vesicles, resulting in congestive edema of the vesicular walls. In severe cases, it may cause structural damage to the vesicular walls, even rupturing small blood vessels. Pathogen-induced inflammation triggers local tissue necrosis, sloughing, and exudative changes.
These pathological alterations lead to capillary dilation and increased permeability in the seminal vesicle walls, ultimately causing vascular rupture. The subsequent blood leakage into urine manifests as terminal hematuria (characterized by blood appearing in the final drops of voided urine). When blood mixes with semen, it presents as hematospermia.
However, if the patient has conditions such as ureteral calculi or bladder cancer, hematuria may also occur due to ulceration on the surface of calculi or tumors. Therefore, further ultrasonographic examination is required to exclude these potential etiologies. After being diagnosed with seminal vesiculitis, patients should avoid excessive fatigue and pay attention to personal hygiene to prevent aggravation of the condition while maintaining good personal hygiene habits to prevent infection.
Treatment Methods for Seminal Vesiculitis
Hematospermia caused by seminal vesiculitis can be treated with antibiotic therapy, hemostatic drugs, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) regulation, seminal vesicle massage, and transrectal ultrasound-guided puncture drainage.
1. Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotics control infection by inhibiting bacterial growth. Common drugs include cephalosporins and quinolones. This is the preferred treatment option for patients with evidence of bacterial infection.
2. Hemostatic Drugs
Hemostatic drugs can assist in reducing bleeding symptoms. Examples: aminocaproic acid and tranexamic acid. It can be considered for use when hematuria is accompanied by active bleeding.
3. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Method
TCM like Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill improves blood circulation and promotes inflammation absorption. It is suitable for mild hematuria in chronic cases or patients allergic to Western medicine.
4. Seminal Vesicle Massage
Seminal vesicle massage can facilitate the discharge of seminal fluid, which is beneficial for reducing inflammation and alleviating hematuria. The specific techniques should be guided by a doctor. It is suitable for cases of mild hematuria without any contraindications.
5. Daily Diet
Patients with seminal vesicle inflammation should pay attention to a healthy diet and avoid eating spicy and irritating foods such as chili peppers and garlic. At the same time, they can consume nutritious foods like pumpkin porridge, egg custard, apples, and kiwis to enhance their immunity.
6. Transrectal Ultrasound-Guided Puncture Drainage
This procedure involves inserting a guide needle into the affected area under imaging guidance to aspirate fluid, thereby achieving decompression. It is mainly targeted at patients with severe hematuria in the acute stage who have no response to conservative treatment.
During treatment, it is necessary to maintain good personal hygiene habits. Clean the external genital area daily and change underwear frequently to reduce the chance of bacterial growth. In terms of diet, it is advisable to have a light diet, avoid spicy and irritating foods, and drink plenty of water, which is beneficial for promoting the excretion of toxins in the body.
How to Prevent Seminal Vesiculitis
- Treat urinary tract infections promptly.
- Drink plenty of water, but older people should drink water appropriately and avoid holding urine.
- Keep a light diet, quit smoking, and drink alcohol moderately (for older adults, avoid alcohol consumption).
- Practice Kegel exercises to improve blood flow.
- Avoid holding urine to reduce the risk of reflux; keep the lower urinary tract unobstructed.
- Have regular physical examinations, conduct comprehensive physical check-ups at regular intervals, and conduct targeted check-ups based on abnormal results from the physical examinations.
- When symptoms such as difficulty in urination and narrow urine stream occur, seek timely medical attention and receive appropriate treatment.
Think of seminal vesiculitis as the "common cold" of the male reproductive system—annoying but manageable. With prompt diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, most men can recover fully and prevent recurrence.



