Complications and Management of Urinary Retention
Date:2019-08-28 click:0
Urinary retention refers to the fact that a full bladder filled with urine and cannot be discharged normally. Urinary retention is a secondary disease. When it occurs, new diseases will occur because urine cannot be drained or urine excretion is limited. Including the following:
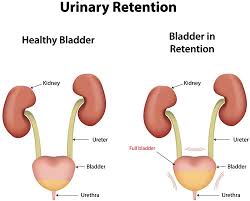
Complications of urinary retention
(1) Infection
The increase of residual urine makes bacteria easy to reproduce, the scouring effect of urine is significantly weakened, and the immune function of the urinary system will be reduced. Infections of the urinary and reproductive systems, such as cystitis, upper urinary tract infection, or acute and chronic epididymitis, are prone to occur.
Patients can use Diuretic and Anti-inflammatory Pill, which can effectively kill a variety of bacteria, viruses, pathogens without side effects. It can diminish the inflammation in the male urogenital system and help patients improve the reproductive system environment and immunity.
(2) Bladder stones
Under normal circumstances, crystalline components of urine, such as calcium oxalate, calcium carbonate, may form micro-stones, but it can be excreted with urine. When the urination of BPH patients is obstructed, the microlithiasis will accumulate more and more, and eventually form bladder stones. Bladder outlet obstruction has a 10% risk causing bladder stones, resulting in sudden interruption of urination, microscopic hematuria, and obvious urinary pain.
(3) Hydronephrosis
Urine is produced by the kidney and passes through the pelvis- ureter-bladder-urethra. If you cannot discharge urine effectively when the bladder is full. Urine will accumulate in the renal pelvis, leading to hydronephrosis, and oppressing the renal parenchyma, impairing renal function.
(4) Renal insufficiency
For patients who have a long course of the condition and can not receive proper treatment. The bladder is in a high-pressure state for a long time. Through the reverse transmission of pressure, the pressure of bilateral pelvis and ureter increases gradually, and the function of the kidney is damaged, which can eventually lead to hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency, even uremia.
(5) Others
Long-term dysuria leads to increased abdominal pressure, which can be accompanied by an inguinal hernia, anal prolapse, or internal hemorrhoids.
Treatment of urinary retention
(1) Hot compress
Hot compress on the suprapubic bladder area and perineum has a good effect on patients with the mild condition. If you have micturition desire in hot water, you can try urinating in the water.
(2) Massage
Gently massage along the umbilical cord to the midpoint of the pubic symphysis, and gradually pressurize. The thumb point can be used to press Guanyuan point for about 1 minute, and gently press the bladder from the upper part of the bladder down with the palm to assist in urination. Do not use too much force to avoid bladder rupture.
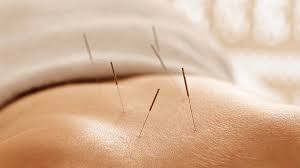
(3) Acupuncture and moxibustion therapy
Guanyuan, Middle-extreme, Yanglingquan, Sanyinjiao, and Sanjiaoshu points can be selected to stimulate with moderate intensity, reinforcing, and reducing simultaneously. The needle can be retained for 10 minutes, and urination can occur after 30 minutes.
(4) Umbilical application therapy
Stir-fry 250 grams of salt, ironing the umbilical belly with a cloth wrap, then apply to the navel after cooling. Or use one garlic, three gardenias, a little salt mashed, put them on a piece of paper and spread on the navel.



